What is Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in Project Management

The PMBOK® Guide (3e) defines Work Breakdown Structure as “a deliverable-oriented hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. It organizes and defines the total scope of the project.
Each descending level represents an increasingly detailed definition of the project work. The WBS is decomposed into work packages. The deliverable orientation of the hierarchy includes both internal and external deliverables.”
Clearly, that’s quite a mouthful.
If you are on a mission to better understand Work Breakdown Structure in project management, then you’ve arrived at your destination!
Here is a complete breakdown of the Work Breakdown Structure – starting from definition to examples to tools. So, let’s get started!
Work Breakdown Structure: Definition and types
Work Breakdown Structure definition is pretty much synchronous with its name – it is the visual disintegration of a project into smaller standalone components that you can manage, evaluate, and assign to teams. Think of it as “divide and conquer” in action.
A good Work Breakdown Structure possesses the following characteristics:
- It is definable and describable so that all project participants understand it.
- It is manageable with a specific authority responsible for overseeing the completion of the meaningful unit of work.
- It is estimable, be it in terms of cost, time, or resources required for completion.
- It is independent with minimum dependence on ongoing work. At the same time, it can be integrated with the entire project.
- It is measurable so that you can track progress, either through the project duration, deliverables, milestones, etc.
- It is adaptable so that you can pivot with the change in project scope if any.
Based on the above description, it becomes clear that the Work Breakdown Structure typically hinges on deliverables or work packages based on duration. As such, one can classify Work Breakdown Structure in project management into the following two types:
- Deliverable-Based Work Breakdown Structure: It draws a clear and direct link between project deliverables with the project scope. As such, you will have to decompose your project into deliverables that contribute to project completion.
- Phase-Based Work Breakdown Structure: This type of WBS in project management divides the project into phases containing work packages. These work packages comprise groups of tasks that are to be completed in stages.
The deliverable-based WBS is more commonly used in project management. On the other hand, phase-based WBS is typically used in projects that do not have clearly defined outcomes.
Importance of Work Breakdown Structure in project management
The value and importance of Work Breakdown Structure can be summarized into the following points:
- Divides the project into smaller, manageable chunks.
- Assists in clearly defining the project scope amongst the stakeholders while also mitigating scope creep.
- The duration or budget of each task can be accounted for to get a near-accurate estimate for the entire project.
- Offers a bird’s eye view of the project as a whole and in part, which makes it easier to visualize progress across the organization.
- Defines specific and measurable outcomes and links them directly to teams and individuals by assigning responsibility.
- By aiding project organization, WBS in project management templatizes success and makes it repeatable.
- Ensures that there are no gaps or overlaps in resource allocation to finetune team performance.
- Facilitates the tandem completion of different and unrelated tasks or work packages, which improves productivity.
- Helps manage dependencies and prevents them from affecting the project delivery timeline or budgets.
- Allows some degree of flexibility during project development while also empowering project managers to compute variations with changes to scope.
How to create a Work Breakdown Structure
From the previous section, it is evident that a Work Breakdown Structure plays a crucial role in successful project management. As such, you may be itching to get started with the creation of a Work Breakdown Structure. Well, we’ve got you covered. Here’s a low-down on how to create a WBS in project management:
1. Define the project scope
Start by identifying the overarching objective that you are trying to meet through this project. Do you have to build a software application? Or mass-produce an item from scratch? Do you wish to get more views on your website? Or upsell products at the payment counter?
Understand the larger picture and use it to define the project scope. You will need the active participation of your entire team at this stage (and for the successive one), as the inputs you receive from them will help determine project goals and the rules governing them. Document all your findings and incorporate the key ones in the project charter.
If you have already prepared documentation like the project scope statement, scope management plan, and project charter, keep these at hand while preparing the Work Breakdown Structure.
2. List down the deliverables or phases
Once the end goal is ready, you have to chart the journey to getting there, along with the milestones you will touch along the way. Divide the project roadmap – from initiation to completion – into distinct phases that break down the project scope statement.
Each phase should amount to something and will be bound by an outcome, duration, or team. At the same time, you will have to map out the deliverables and sub-deliverables that will be generated at various junctures as the project progresses.
Also, define the specifications of the deliverables for a specific task to be deemed complete. Feel free to create control accounts, which constitute task categories for the different areas of work that you would like to monitor.
3. Establish the WBS levels
Now that you have the project goal and the deliverables and phases propping it up, it is time to arrange them in a hierarchical and logical ladder. Generally speaking, WBS in project management is limited to a maximum of three levels, these are:
- Parent Task: Also known as the project objective, the parent task offers a broad overview of the basic goal of the project.
- Dependencies and Tasks: These contain dependencies that lend slightly more granularity to the parent task.
- Subdependencies and subtasks: The third and the lowest level of a Work Breakdown Structure defines the task in the highest detail.
Of course, the three-tiered structure of Work Breakdown Structure in project management is followed as a rule of thumb and can be expanded or elaborated upon depending on the project.
4. Prepare a WBS dictionary
Given the visual nature of the Work Breakdown Structure, it only contains the skeleton outline and omits a detailed explanation of the tasks. Accordingly, the WBS must be read along with the WBS dictionary.
As the name suggests, the WBS dictionary gives language and meaning to the terms used in your Work Breakdown Structure, specifically to the work package at the lowest level. It contains key definitions and scopes of the different elements present in the WBS, such as the work package names, task owners, IDs, deliverables, due dates, status, budgets, risks, etc.
Resultantly, the entire team can be on the same page and use standardized terminologies so that there is no room for ambiguity.
Components of a Work Breakdown Structure [with example]
Now that you know how to create a Work Breakdown Structure and go about testing this knowledge, allow us to elaborate on the elements of a typical Work Breakdown Structure. Here are some details that a WBS in project management should ideally contain:
- Task Identifier: A unique name, number, title, or description to ID the task to prevent task duplication.
- Task Owner: Details of the team/individual responsible for completing the task.
- Task Dependency: Linkage between two related tasks where the completion of one has bearings on the other.
- Start and Finish Dates: Ideal timeline for the completion of the task.
- Duration: Number of days/hours required to complete the task.
- Work Progress: Contribution of the task to the entire project (usually denoted in %).
- Task Status: Whether the task is assigned, in progress, completed, late, etc.
Here is a Work Breakdown Structure example for the construction of a house to illustrate these individual components:
As you can see, not everything recommended above has been used as the WBS for the construction of a house is pretty simple. However, you will see the emergence of task IDs, dependencies, timelines, and more details.
Types of Work Breakdown Structure charts
There are different ways to illustrate Work Breakdown Structures. Here are a few popular Work Breakdown Structure examples that will shed light on the different formats in which you can display the WBS:
1. Work Breakdown Structure list
The Structure List is the simplest form of WBS in project management. It shows the hierarchical structure of the WBS in the form of a numbered list, which decomposes further into sub-numbered lists and so on.
While it is the simplest form of Work Breakdown Structure, fleshing out the details of the task, such as the budget, assignment, duration, etc., is difficult in this format.
2. Work Breakdown Structure tree diagram
The WBS tree diagram denotes the hierarchy of tasks and subtasks by positioning them at different levels. It follows a top-down approach with Level 1 or the parent task at the top and the project branching off into multiple tasks/dependencies and subtasks/sub-dependencies. Tree Diagrams are the commonest depictions of the Work Breakdown Structure.
3. Work Breakdown Structure flowcharts
WBS flowcharts are a variation of the tree diagram wherein the workflow is indicated through arrows. These connectors are a great replacement for a simple line as they organize the WBS sequentially.
Plus, they are far more flexible, whether you have a simple Work Breakdown Structure or a complicated one with dependencies and if-then-else scenarios.
4. Work Breakdown Structure spreadsheet
If you can pivot your Work Breakdown Structure into rows and columns, then spreadsheets would be an excellent format for your WBS. They offer almost infinite space, and you can incorporate details, data, and more.
Further, you can program the spreadsheet to manage dependencies and highlight changes as the project progresses.
5. Work Breakdown Structure Gantt chart
Gantt charts are an advanced form of timelines and spreadsheets used to depict Work Breakdown Structure. It is presented as a bar chart that tracks tasks along the time axis.
As a result, it visually marks the start date and finish date of the task. Based on the dependencies, you can schedule the tasks one after the other or in parallel to create a critical path for maximum efficiency.
With Nifty, you can generate Gantt charts with a click of a button. Change the view from Tasks to milestones, and the chart will be generated automatically.
5 Excellent WBS Tools
There are several agile project management tools available in the market that make WBS creation child’s play. However, the sheer number of options can hamstring decision-making.
Here are some of our top picks to spare you the pain and effort of separating grain from the chaff:
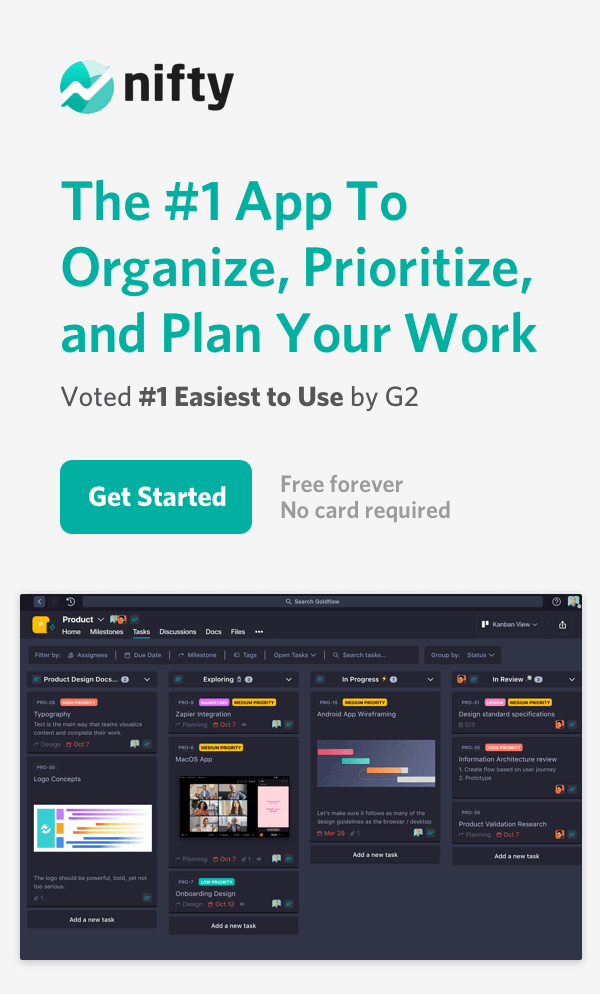
1. Nifty
Nifty is your one-stop shop for all things project management. The project management OS specializes in project charts and allows users to choose from an assortment of WBS formats, from the very popular Gantt Chart or Kanban Board to the lesser-known Pie Charts and Control Charts. Make your pick and get started – it is that easy!
2. Monday
Monday.com is a powerful Work OS that allows WBS creation in different formats like Gantt Chart, Kanban Board, etc. It also offers a variety of WBS templates that you can customize.
3. Wrike
Wrike is a cloud-based enterprise project management software focusing on team collaboration. You can use it to create WBS in project management as task lists, Gantt charts, flowcharts, and more.
4. Asana
Asana is a popular cloud-based project management tool that enables teams to work collaboratively on projects and tasks. It comes with task lists, drag-and-drop assignments, and a calendar view, which makes WBS creation simple.
5. Trello
Trello utilizes the Kanban methodology of project management. As such, you can use card views, task boards, due dates, etc., to prepare the WBS and monitor it in real-time.
Prevent project breakdown with Work Breakdown Structure
Work Breakdown Structure makes project success a habit. Plus, with the right tools creating a WBS is not even hard! Once you get the hang of it, you will find the visual nature of WBS to be highly informative and helpful in supercharging project development. So, why miss out on such an opportunity? Get started with Nifty for free!