What is PMO (Project Management Office)?

We’re in the thick of the Project Economy, and the PMO—or Project Management Office department—is in the spotlight. Rightly so.
As organizations strive to achieve excellence in project delivery, the role of a PMO is more important than ever. A portfolio management office (PfMO) plays a crucial role in coordinating the management of portfolio components and ensuring alignment with organizational objectives.
However, not everyone understands the true value PMO brings to the table. Reportedly, 93% of unsupported PMOs claim executives lack an understanding of PMO value. To make matters worse, 70% of Project Management Office’s don’t have a formal process for assessing value.
In this advanced guide, we’ll cover everything PMO-related—from what the Project Management Office (PMO) is to how it benefits your organization tangibly. Let’s go!
What is Project Management Office PMO?
A PMO (short for project management office) refers to an internal or external group that defines—and monitors—project management best practices and standards within a company.
According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), PMOs are responsible for documenting project progress and strategy, as outlined in PMI’s standards such as The Standard for Portfolio Management, The Standard for Program Management, and A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), to ensure there are no project delays whatsoever.
Think of them as gatekeepers of all things project-related, such as documentation, key performance indicators, metrics, tasks, team performance, etc., to ensure seamless, on-time, and within-budget project delivery.
✨ Try Nifty, your virtual PMO assistant.
Get Started for Free
PMO Roles and Responsibilities: What Does PMO Do?
The PMO team is an organization’s driving force. They help move the needles across challenging projects and offer end-to-end visibility into how well the project is shaping up.
Here’s an overview of the key roles and responsibilities of a Project Management Office:
- Resource Management: A project management office manages and allocates company resources across various activities and projects. This is usually done based on organizational priorities and budget.
- Planning and Governance: A PMO can be tasked with choosing investment projects that support organizational objectives, outlining the criteria for every project, and advising the management on the project’s ROI. Accordingly, a PMO ensures the management makes the right decisions based on accurate information. Program management is crucial in guiding project management initiatives and supporting strategic planning.
- Organizational Culture: A PMO can enhance organizational culture by setting project culture by communicating and training employees on methods and best practices.
- Transparency: A PMO offers accurate and relevant information about projects to support organizational decision-making, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Support: PMOs are typically created to facilitate project execution. This is mainly done by helping project teams, facilitating effective implementation of strategies, training employees, and monitoring progress. The PMO also ensures that project management best practices are met.
Types of Project Management Offices PMOs

PMOs differ in every department and organization. Accordingly, they perform different tasks and perform their roles in unique ways. Typically, PMOs are categorized as:
1. Controlling Project Management Office
This type of project management office effectively evaluates the application and use of various processes, methods, tools, and standards. The PMO may also control how strategies are applied by outlining a guideline for work completion.
2. Supportive Project Management Office
This type of PMO supports development projects and company activities by collecting project information, outlining best practices, training employees, and advising top management. A supportive PMO does not exercise control over projects and activities.
3. Directive Project Management Office
This PMO controls the most significant part of projects within a company. The PMO offers directives on all aspects of the project and evaluates performance over time.
Use Nifty for all your PMO planning.
Get Started Free
PMO vs Project Manager: Is There a Difference?
At the outset, the functions of a project management office vs project manager may seem the same—and functionally, they are to some extent. However, there are distinct differences between the two:
- Focus: A project manager is an individual who handles a project from start to end, whereas PMO is a team of experts who work on a project at an organizational level, ensuring the right projects are prioritized and are in perfect alignment with the company’s objectives.
Additionally, project and program managers often report to the PMO, which provides support functions and manages day-to-day operations related to project and program management. - Duties: A project manager defines the project goals, collects data, schedules tasks, and monitors the project’s timelines, budgets, and resources. A PMO’s duties are larger in scope and multidisciplinary in nature.
A PMO brings together different contributing teams, such as finance, IT, planning, risk management, and resourcing, to ensure all organizational projects are delivered without compromising on quality. By extension, a PMO maps out project objectives and scope, defines standards and processes, curates the workflow, brainstorms on methodologies, and tackles crippling issues such as resource constraints.
What Is PMO Software?
Office project management tools are often viewed as added (read: unnecessary) cost, but they do add value if leveraged properly.
But what is Project Management Office software exactly?
PMO (Project Management Office) software helps you manage your projects and portfolios more efficiently so that you can focus on what matters the most from day one. It wouldn’t be wrong to say that the PMO software doubles up as a trusted sidekick for the team, ensuring every step of your project is executed seamlessly, from start to finish.
Additionally, PMO software helps streamline project management processes to ensure projects are completed on time and within budget.
Aside from project planning, PMO software offers useful features like analytics, tracking, planning, resource allocation, prioritization, scheduling, and reporting. These features help you understand your business’s performance and make decisions that can quickly gain stakeholder buy-in.
Try the best PMO software for free. Get Started
What Makes a Great PMO Software?
A robust PMO software should have the following features these are table stakes to ensure the team is always working on high-impact projects (as opposed to working on low-priority tasks):
- Flexibility: A flexible PMO software allows you to adjust to changes easily—whether it’s customer expectations, business policy changes, and so on. In simpler words, it gives your stakeholders what they want, without compromising on project quality or timelines.
- Team Management + Collaboration: Perhaps the biggest advantage of using PMO software is increased collaboration as teams work as one and communicate in real-time.
- Support for Methodologies: PMO software should adapt to the project management methodology that best suits your projects (and not the other way around).
- Resource Management: It helps manage your resources effectively so that the teams don’t experience overwhelm or worse, burnout!
- Dashboards for Performance Monitoring: A custom PMO software offers comprehensive dashboards that throw light on how well your projects are doing and provides insights into where to make improvements. A data-backed approach allows your projects to get completed to everyone’s level of satisfaction.
At the end of the day, choosing the right PMO software is most important. However, make sure to account for the features you need basis your specific business use cases. There are many options available to help you manage your projects intelligently. One such software is Nifty (more on this in the next section).
Nifty: An All-in-One PMO Software for IT and Project Management Teams
Nifty is a PMO software that offers a mix of essential project management features such as resource management, workload management, task management, etc., and advanced project portfolio functionalities. Training the project management team is crucial for the effective functioning of the PMO, as it involves coaching, mentoring, and oversight.
You can automate simple, repetitive tasks and empower the team to work speedily. So, even if the deadlines get aggressive mid-way, you won’t be left scrambling for more resources or budget.
Let’s dive deep to understand how each feature drives better visibility into teams and enhances workflows.
Real-Time Project Management
In any effective PMO software, real-time functionality is everything—in that, you can see updates as they occur and get your teams to work together as a well-oiled machine.
Our project management software operates in the cloud and updates instantly. This ensures teams are aware of their tasks, provides transparency into processes, and helps your projects to run smoothly.
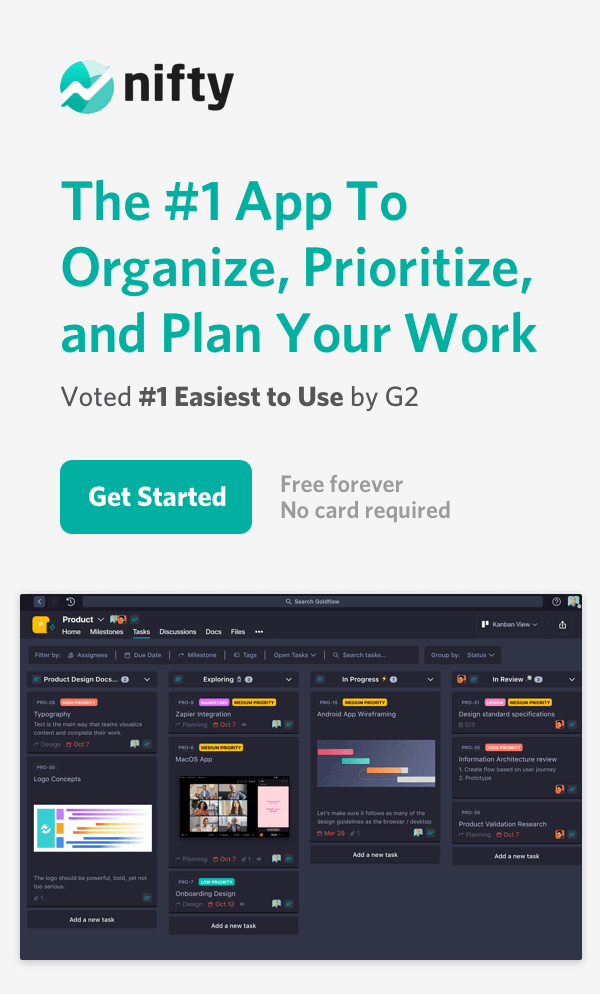
Let’s say you want to prioritize product features for an upcoming website launch. Nifty’s real-time project management allows you to create custom story maps using different views like Kanban, List, or Swimlane.
And if you want real-time updates on tasks or visibility into task status, due dates, or assignee details, Nifty offers a bird-eye view of your project in one centralized place.
You know what this means, right? You can manage dependencies and scope creep on the fly! And if you’re visually driven, you can also color-code projects and tasks. One glance and the team will understand the level of effort needed for the specific task at hand.
Try the best PMO software for free.
Get Started
Project Portfolio Management
Want to organize your projects and structure teams for an elevated project management experience? Nifty’s project portfolio management feature is just what you need.
A program management office (PgMO) plays a crucial role in managing projects and programs by overseeing their execution, ensuring alignment with strategic goals, and optimizing resource allocation.
PMOs typically deal with multiple inter-connected projects at a time. Instead of wasting time going into each project separately, Nifty gives you an overview of all your current projects to help you plan projects like a pro.
In other words, use Nifty to see your projects from different angles. For example, there’s an overview feature that gives you a high-level look at all your projects. You can organize them in any format of choice and group them into folders or even create new ones for clients who need extra attention.
Nifty’s project portfolio management feature comes in handy for:
- Foldering projects into portfolio teams based on specific criteria and roles such as operations, account ownership, client delivery, and so on
- Viewing all projects in your Portfolio, along with their updated status and list of participants from a single source of truth
- Controlling participation within projects using the Public or Private setting where you can send invitations for projects within a Portfolio and manually control a project’s privacy
- Changing project ownership by allowing you to move projects across Portfolios and personalizing the workspace based on your unique use case
A real-time project portfolio dashboard like Nifty tracks progress across key project metrics, showing colorful graphs and charts that are easy to share. Automated reports on status, tasks, and timelines can also provide more detailed data.
That’s not all. You can generate in-depth project descriptions, create tasks and action items, etc., making portfolio management a breeze. Remember, most projects seldom work in isolation, having a portfolio view makes it all the more easier to view everything on one screen.
Project Portfolio Roadmap

When you need to ensure that every task meets requirements across all projects and standardize processes, detailed data can be a game-changer.
Nifty’s portfolio roadmap offers a comprehensive view of every project in your PMO. Projects are displayed on a timeline in a Gantt chart view, allowing you to see each project at the task level. So, if you need to build a visual roadmap for your product and automate progress tracking, you can use this feature without a second thought:

You can filter the Gantt chart by assignee, project manager, or customer to focus on the specific information you need. As you can imagine, this capability helps you make more accurate forecasts for your PMO.
Resource Management

Managing resources for a project involves handling staff, equipment, materials, and more. And that’s just for one project. When you manage resources at the PMO level, you can ensure that all your projects have the resources they need to keep moving forward.
Nifty’s resource management feature allows you to track, manage, and report on resources across your portfolio. You’ll have visibility into your resources and can ensure they’re balanced so each project gets what it needs when it needs it.
Because our software is cloud-based, you can track your project’s performance against the planned work to ensure you’re staying on schedule.
Workload Management

Team workloads vary wildly as the project progresses, and if you’re not keeping a close eye on who is doing what, teams can become overworked or underworked, which isn’t good for productivity or morale.
Ask any project manager, and they’ll tell you managing your team’s workload is central to ensuring your tasks are well-balanced. Whether you want to change the existing resource load or add new members entirely, Nifty’s workload management feature makes it easy on all accounts.
With Nifty’s workload management feature, you get transparency into the workload of all your projects through easy-to-use, color-coded pages.
You can quickly see who is overallocated and then reallocate resources right from the workload page to balance the team’s workload. It’s that simple: optimize resources in real time.
This allows you to make data-driven decisions to better manage your teams across multiple projects.
How Can a Project Management Office Benefit Your Organization?
Now that you understand what a PMO is, let’s look at why having one can benefit your organization:
- Guidance: A PMO helps align your projects with the organization’s long-term strategy and standardizes procedures as well as workflows. This way, your projects will be delivered as per the customer’s and organization’s requirements. Additionally, maintaining project management standards across the organization ensures consistency and quality in project execution.
- On-track projects: The PMO acts as a watchdog, using metrics to ensure projects stay on course. They alert you to issues like scheduling or budget problems before they become major roadblocks.
- Big picture view: When managing multiple projects, the PMO sees how they all fit together. This broader view helps you understand how your actions in one project can impact others.
- Seamless communication and better coordination: The PMO helps communicate with stakeholders and ensures your message is heard and understood. They also work with other project participants, improving communication in the process
- Shared resources: By centralizing resources, the PMO ensures they are used efficiently across projects—an especially useful feature when resources are limited but projects are plenty.
- Supported business strategy: When projects align with business goals, the PMO provides various benefits, including training, tools, and mentoring. However, having a PMO alone isn’t enough; you also need skilled people, effective processes, and the right technology to make it work.
- Strategic planning: Modern project managers understand the value true visibility unlocks—they can see which projects are under budget, which ones lack resources, which ones need more productivity, and which ones aren’t in alignment with company goals. PMOs tackle all these areas with great agility and confidence.
But Who Needs a Project Management Office?
Smaller agencies and startups can survive without a PMO, but the same cannot be said for larger organizations with cross-functional (and often conflicting) projects.
Sure, not every company will have a dedicated PMO team, but if your organization is dealing with incrementally growing projects, having a PMO will be useful.
Program management offices (PMOs) can be categorized into different tiers. A Tier-Three PMO performs functions at the portfolio level, directing and managing projects and programs to ensure they are aligned with organizational strategy and deliver anticipated benefits.
Additionally, the Tier-Three PMO advises senior management at the business strategy level, demonstrating the comprehensive nature of program management within the PMO framework.
In essence, you must set up a PMO if you want to:
- Understand how every ongoing project fits into the overall company strategy
- Allocate resources optimally without risking project delay or, worse, failure
- Complete projects on time and within the stipulated budget
- Your stakeholders to have complete visibility into project status and performance
- A standardized workflow and process for completing projects
- Track project success accurately with real-time data
- Keep the team in the loop with relevant training on project culture, work processes, etc.
- Standardize project decisions and drive informed decisions with everyone in the know
More importantly, for a successful PMO, your team must possess a diverse set of skills. The PMI has highlighted specific power skills that the project management experts must possess. These include communication skills, conflict management, emotional intelligence, empathy, negotiation, problem-solving, and teamwork.
So, in addition to hard-core project management expertise, make sure to account for these soft skills when creating a team from scratch.
Elevate PMO Performance and Champion Collaboration with Nifty
A PMO comprises the right mix of people, processes, and tools.
The trick lies in setting up a PMO with the right leader at the helm of affairs and leveraging complementary PMO software that tackles work that can easily be automated. After all, as the person in charge pushes for unpopular changes, they will not have time to work on the repetitive tasks. This is where a tool like Nifty can take over.
PMO staff support project teams by assisting and aiding project managers in coordinating projects and aligning them with organizational objectives.
Another point to note is that integrating the PMO into the organization’s culture is a gradual process. It requires transparency in the project environment. And the extent to which transparency is embraced in the company culture can either facilitate or impede this transition.
However, once established, a PMO becomes a vital part of the organization. It supports success and provides project managers with a broader perspective, setting the stage for productive teams and successful projects.
Thinking of starting a PMO at your company? Make sure they have the best tools for the job. Sign up for a free trial of Nifty and empower your PMO to make a positive impact on your organization.